Under the auspices of the Indo-German Energy Forum, the vgbe conducted a short study on the retrofitting potential of Indian coal-fired power plants with respect to electro-thermal energy storage.
Electro-thermal energy storage is a concept in which excess electricity is converted into heat – this is the charging process. During discharge, this heat is used to generate electricity using a thermal power process. Such a technology is therefore ideal for the subsequent use of coal-fired power plants so that the existing plant infrastructure can continue to be used.
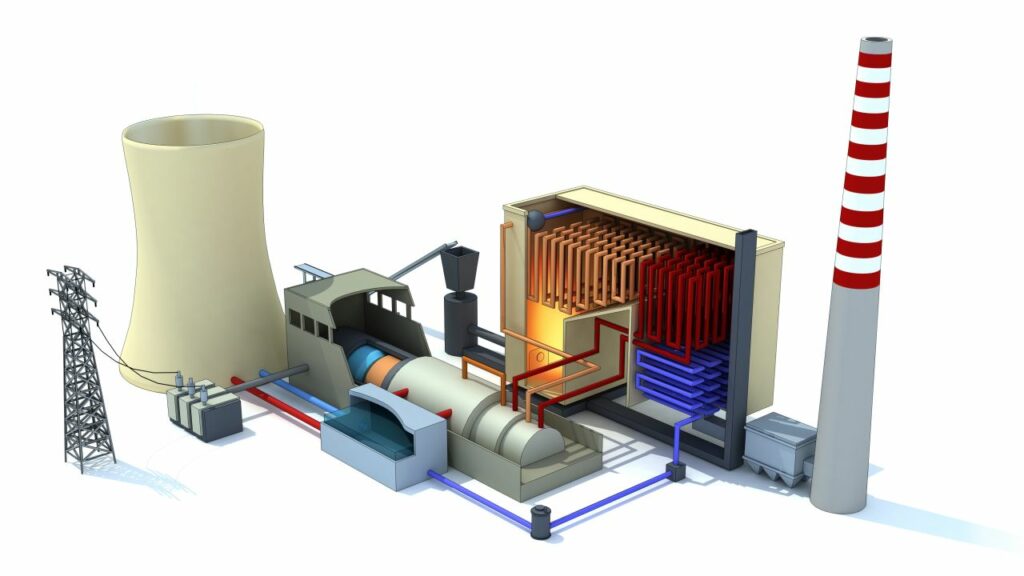
Pilot projects in Chile, Europe and the USA served as the basis for the study. In these projects, technology concepts have prevailed that differ in the type of storage material: molten salt, rock-based and sand-based heat storage concepts. The respective advantages and disadvantages of these technologies in terms of technology readiness level, costs and temperature ranges were compared. All of these concepts are suitable for converting the Indian coal fleet. Due to the climatic conditions in India, long storage charging times can be achieved primarily with the help of photovoltaics.
The study was commissioned by the Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH and led by Prof. Dr. Markus Haider – head of the Institute for Thermodynamics and Energy Conversion at TU Wien and member of vgbe’s Scientific Advisory Board.

Short study: Electro-thermal energy storage – retrofitting potential of coal-fired power plants in India
The report is currently being revised and will be available again shortly.
Contact
Dr.Ing. Claudia Weise: claudia.weise@vgbe.energy